Class G Airspace Visibility Requirements
Sport and recreational aviation activities; Vfr minimum visibility above 10,000 msl:
How To Remember Vfr Weather Minimums - Bobbie Lind
A helicopter may be operated clear of clouds in an airport traffic pattern within 1/2 mile of the runway or helipad of intended landing if the flight visibility is not less than 1/2 statute mile.
Class g airspace visibility requirements. If conditions in class g airspace below 10,000 ft yield a ceiling greater than 1,000 ft but visibility of 2 sm, would be legal to fly vfr in it, given you meet the. One mile visibility and clear of clouds is the daytime requirement. Imc means having less than 3 sm visibility and/or 1,000 ft ceiling.
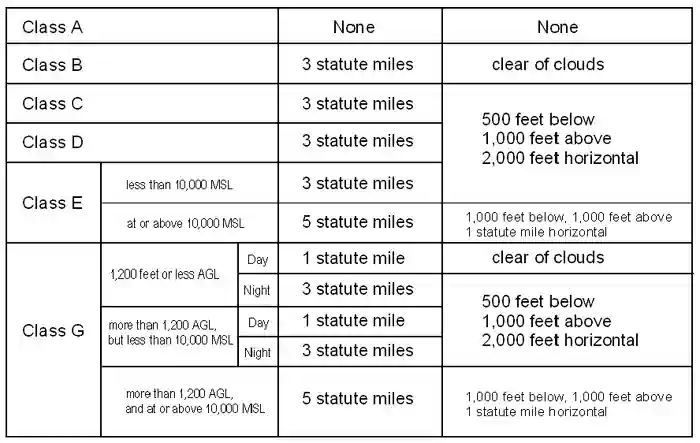
36 rows notwithstanding the provisions of paragraph (a) of this section, the following operations may. Vfr visibility requirements in class g airspace are 1 mile (1.6 km) by day, and 3 miles (5 km) by night, for altitudes below 10,000 feet (3,050 m) msl but above 1,200 ft agl. 1,200 ft agl or below, day.
1,200ft or less above the surface (regardless of msl altitude) day: Above 1200ft, stays at 1sm visibility but then for cloud clearance you must be 1000ft above, 500ft below and 2000ft horizontal. 1 statute mile visibility and clear of clouds
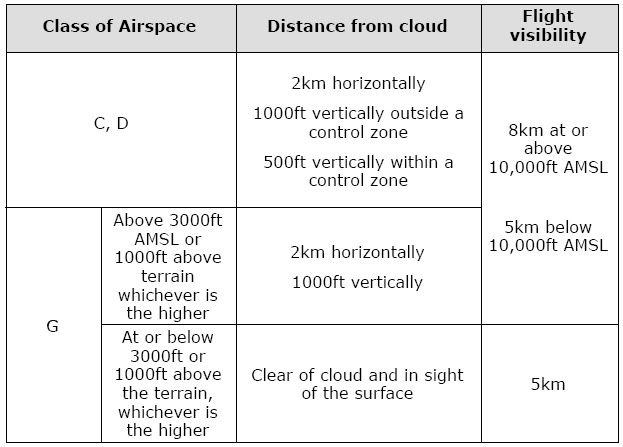
Class g airspace weather & visibility requirements. Above the class g (ground) is class. In accordance with far 91.155:
Both class g vfr visibility requirements below 10,000 ft msl and 1,200 ft agl are 1 sm. Night, except as provided in §91.155(b) 3 statute miles. Class g 1,200 feet or less above the surface (regardless of msl altitude).
Class g airspace is not depicted on any chart; Atc may permit operations in weather conditions that do not meet this criteria (special vfr) source: Class g airspace (uncontrolled) is that portion of airspace that has not been designated as class a, class b, class c, class d, or class e airspace.
Although class g is uncontrolled, it is also subject to the most weather restrictions based on where the airspace is located. There are a few nuances here so pay attention. Class g (uncontrolled) class g is considered uncontrolled airspace, but still has vfr weather minimums.
Day, except as provided in §91.155(b) 1 statute mile. (since you just need to be clear of clouds and 1 sm visibility), you could take off vfr in class g and you couldn't take off in class e. Rules governing vfr flight have been adopted to assist the pilot in meeting the responsibility to see and avoid other aircraft.
For aircraft other than helicopters: 500 feet below 1,000 feet above 2,000 feet horizontal. You can remember class g (uncontrolled airspace) because it's just like the good old days at the dawn of aviation.
Weather requirements class g minimum weather requirements exist so that you can see. In class b airspace aircraft are required to remain clear of clouds. ( a ) unless otherwise specified in the certificate holder's operations specifications, when conducting vfr helicopter air ambulance operations in class g airspace, the weather minimums in the following table apply:
5 statute miles** vfr minimum distance from clouds above 10,000 msl: 1,200 ft agl or below, night. 1,200' or less above the surface (regardless of.
(however, you'd still have to be sure not to be engaged. Classes a, c, d & e are controlled airspace whilst for **classes f & g airspace the uk has registered differences from the icao standard so as to allow greater flexibility to vfr flights at and below 3000ft amsl and to allow ifr flight in this airspace without the requirement to carry a radio. Notwithstanding the provisions of paragraph (a) of this section, the following operations may be conducted in class g airspace below 1,200 feet above the surface:
Or 500 ft vertically below cloud. Class g airspace includes all airspace below 14,500 feet (4,400 m) msl not otherwise classified as controlled. Daytime requirements for class g are 1 statute mile visibility and clear of clouds to 1200ft.
Minimum flight visibility and distance from clouds required for vfr flight are contained in 14 cfr section 91.155. At night, requirements jump to three miles visibility and from merely clear of clouds to 500 feet below, 2,000 feet horizontal, and. § 135.609 vfr ceiling and visibility requirements for class g airspace.
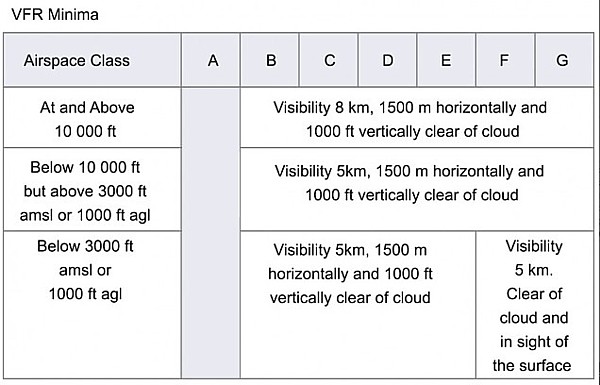
Class e and class g airspace; Airspace flight visibility cloud clearance 10,000 msl e 5 statute miles 111 41,000 below, 41,000 above, 41 smhorizontal c d e b 3 statute miles clear of clouds g (night) 3 statute miles 152 4500 below 41,000 above 42,000 horizontal g (day) 1 statute mile 152 4500 below 41,000 above 42,000 horizontal g (night) 3 statute miles 152 4500 below 41,000 above 42,000 horizontal 600 m horizontal, 1000 ft vertically above cloud;
14 rows these minimums cover most class g airspace, but are only valid during the daytime when. Class g airspace (uncontrolled) is that portion of airspace that has not been designated as class a, class b, class c, class d, or class e airspace. (*no airspace is designated class b in the uk).
Class Golf Airspace
Regulations Vfr Minimums Learn To Fly Blog - Asa Aviation Supplies Academics Inc
Ifr Versus Vfr

Airspace Classification
The Airline Pilots Forum And Resource

Airspace Classes Explained The Ultimate Guide For Beginners

Visual Meteorological Conditions - Wikiwand
How To Remember Vfr Weather Minimums - Bobbie Lind
51asorg

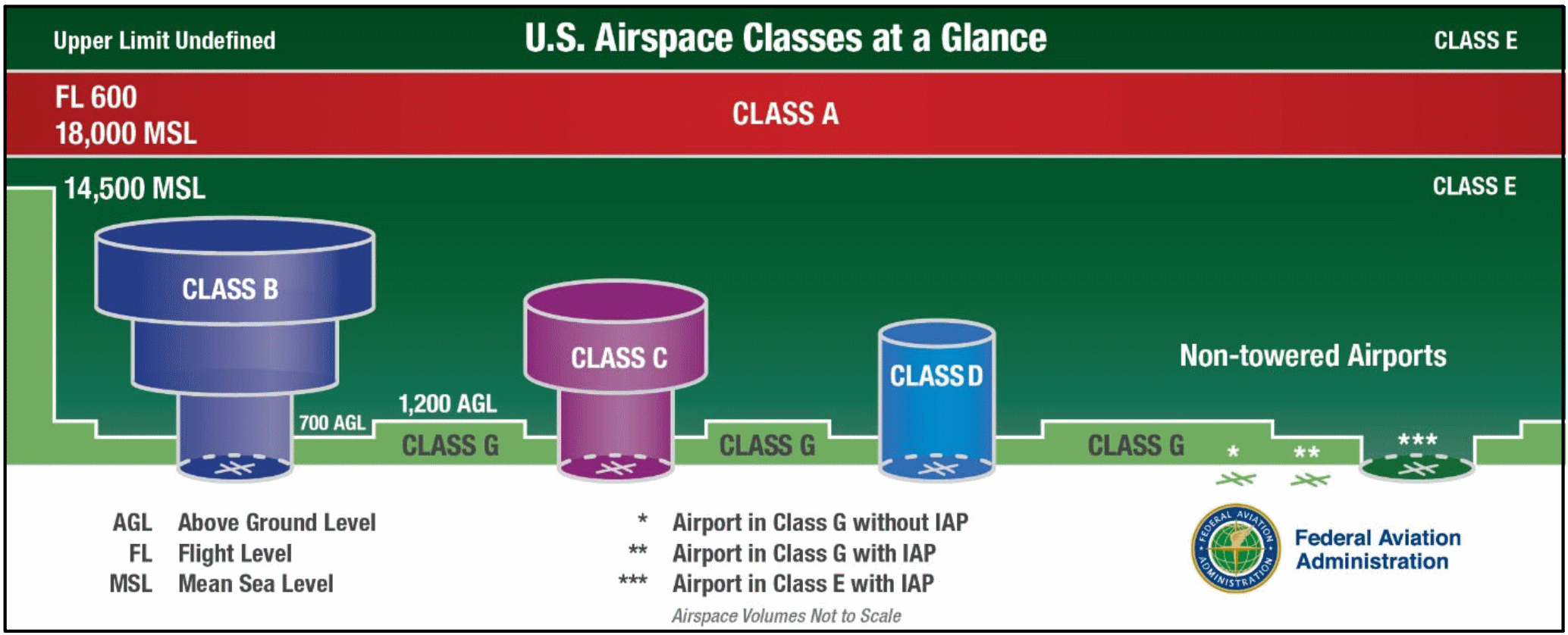
2k National Airspace System

This Is How Class G Airspace Works Boldmethod

This Is How Class G Airspace Works Boldmethod
Special Vfr Svfr
How To Remember Vfr Weather Minimums - Bobbie Lind

Visual Flight Rules

Part 91 Subpart A General Operating And Flight

Cpl Air Law Atc Chapters Ppt Video Online Download

Visual Flight Rules Praditya Ewangga

Helicopter Instrument Procedures Part Three